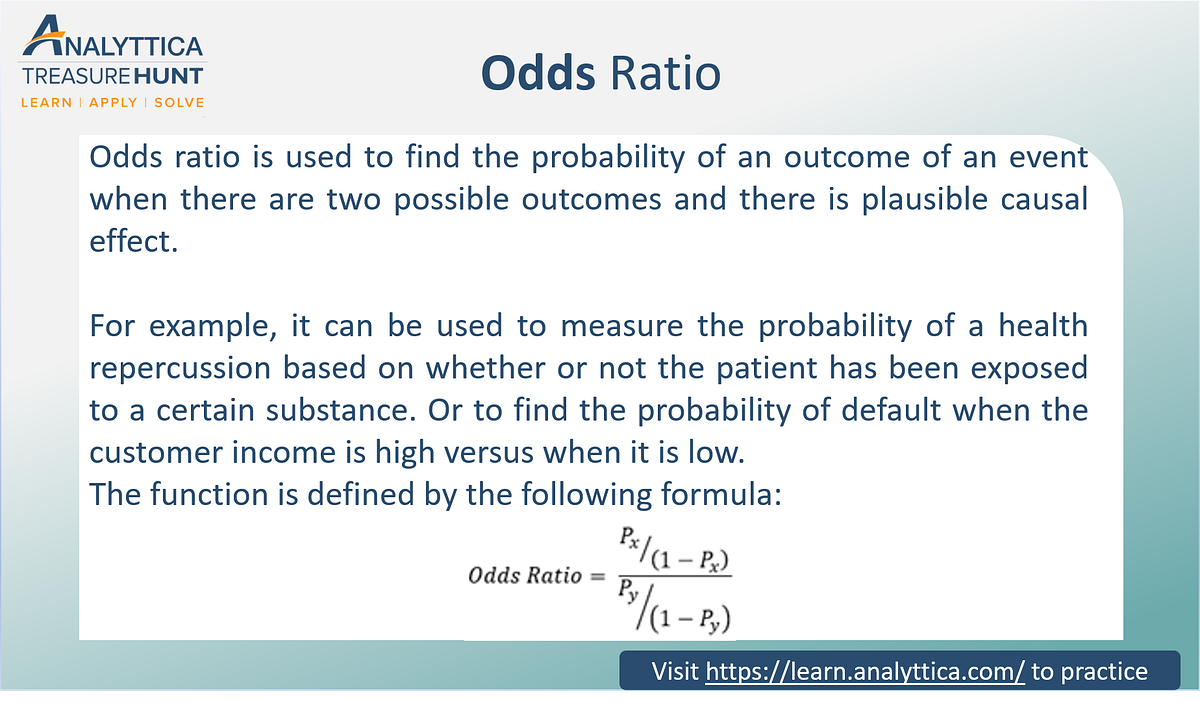
The math underlying odds and gambling can help determine whether a wager is worth pursuing The first thing to understand is that there are three distinct types of For instance, odds are a symmetric measure, meaning that while risk only examines outcomes given interventions, odds can also examine interventions given outcomes Thus, a study can be constructed where, rather than choosing trial groups and measuring outcomes, outcomes can be chosen, and other factors can be analyzedIn biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome "Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the two

Odds Ratios Of Risk Factors For The Severity Of Cad By Ethnicity Odds Download Scientific Diagram
Odds vs risk
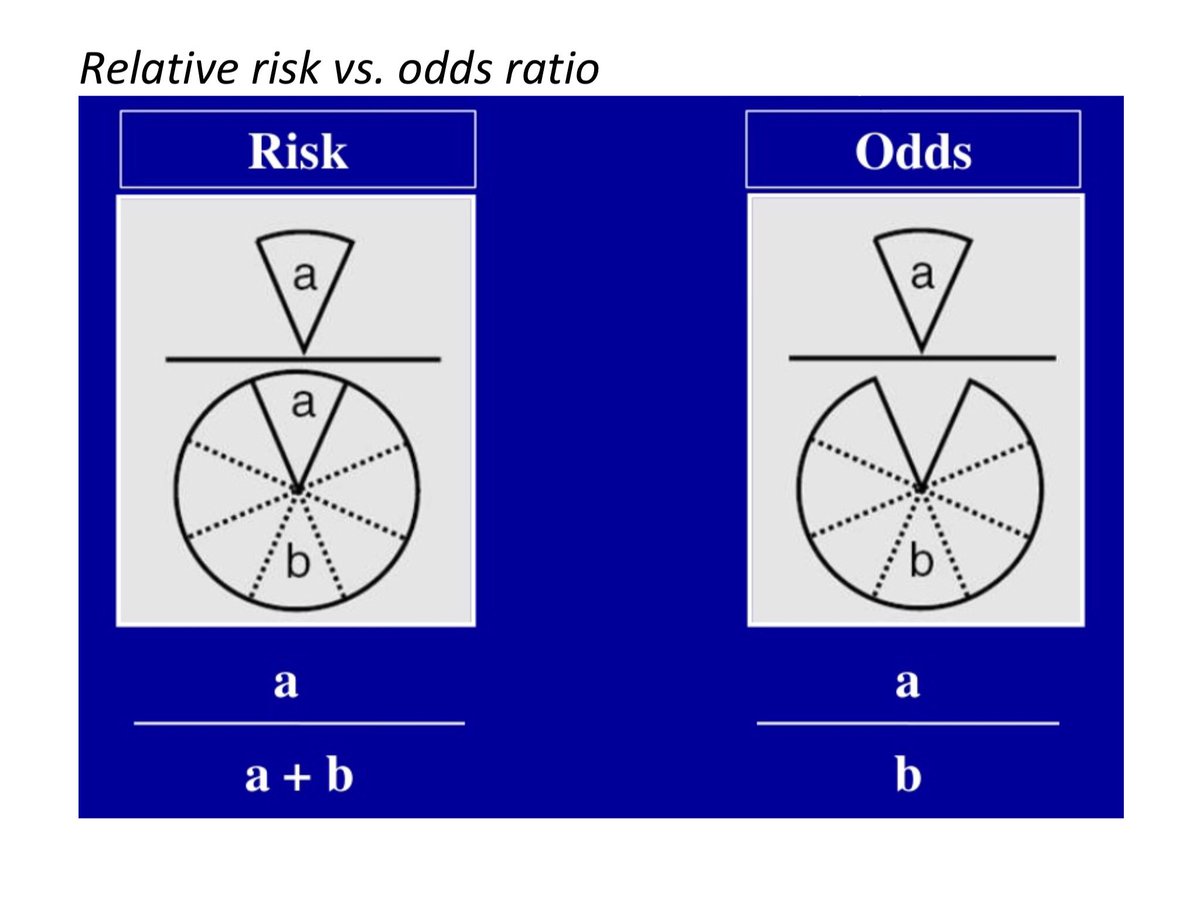
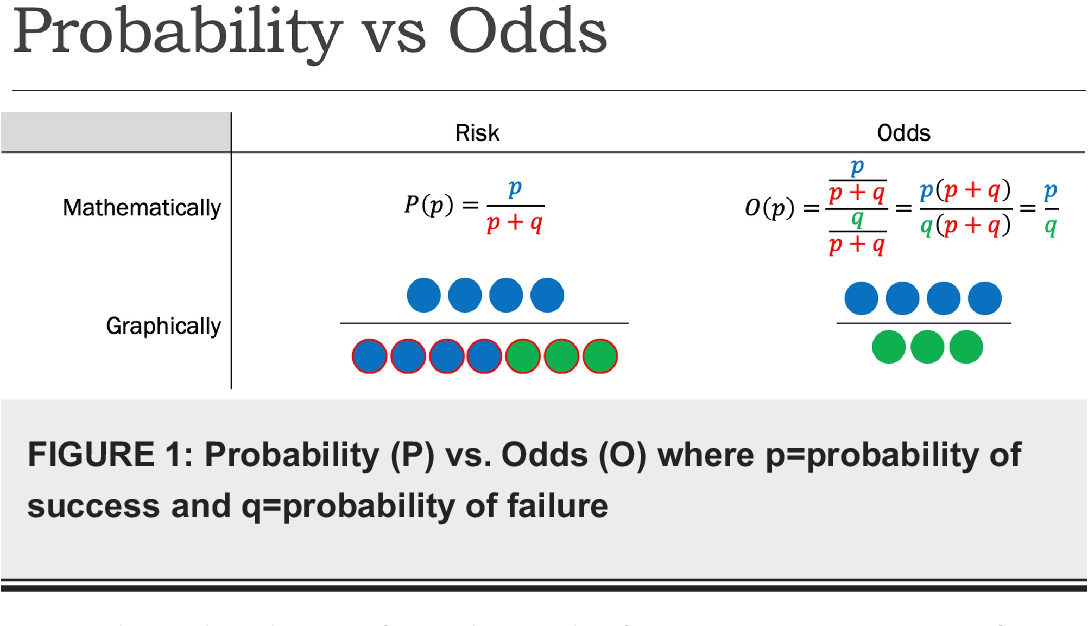
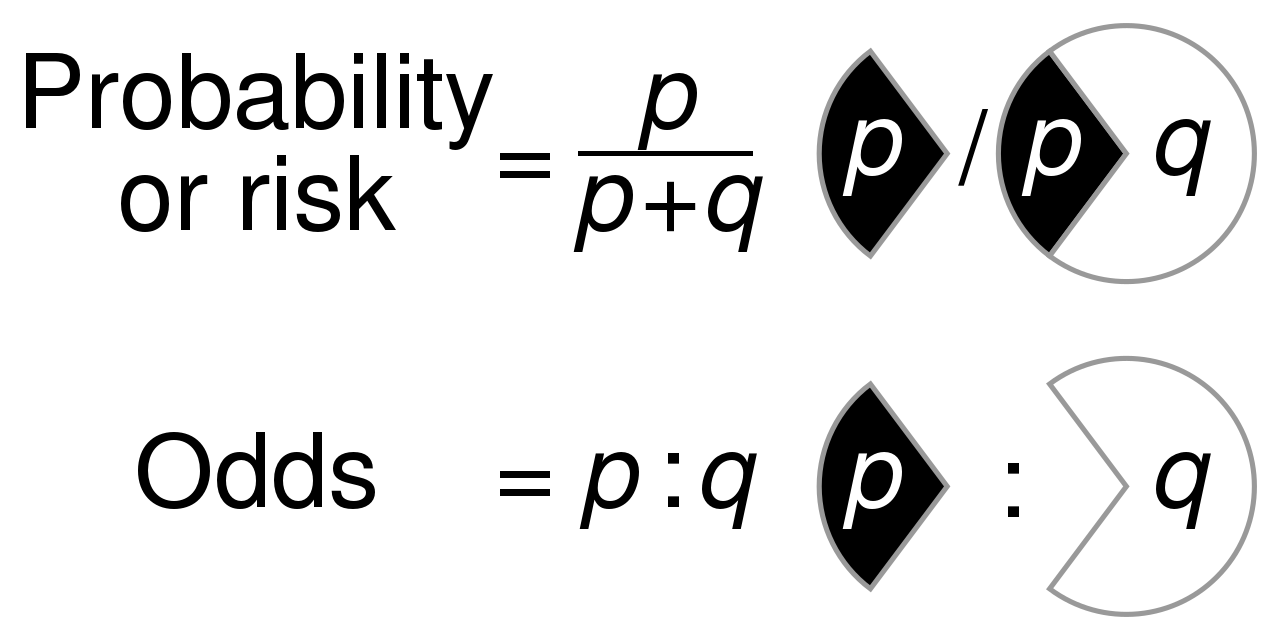
Odds vs risk-RISK AND ODDS DEFINITIONS "Risk" refers to the probability of occurrence of an event or outcome Statistically, risk = chance of the outcome of interest/all possible outcomes The term "odds" is often used instead of risk "Odds" refers to the probability of occurrence of an event/probability of the event not occurringRisks and Odds When talking about the chance of something happening, eg death, hip fracture, we can talk about • risk and relative risk or • odds and odds ratio Risks and odds Risks and odds Risks A proportion Numerator / Denominator Odds A ratio Numerator / (Denominator Numerator) 2 Two by two table




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)63 Risk, Relative Risk and Odds In this section, we will introduce some other measures we can find using a contingency table One of the most straightforward measures to find is the risk of any given event Risk The probability that an event will occur Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction
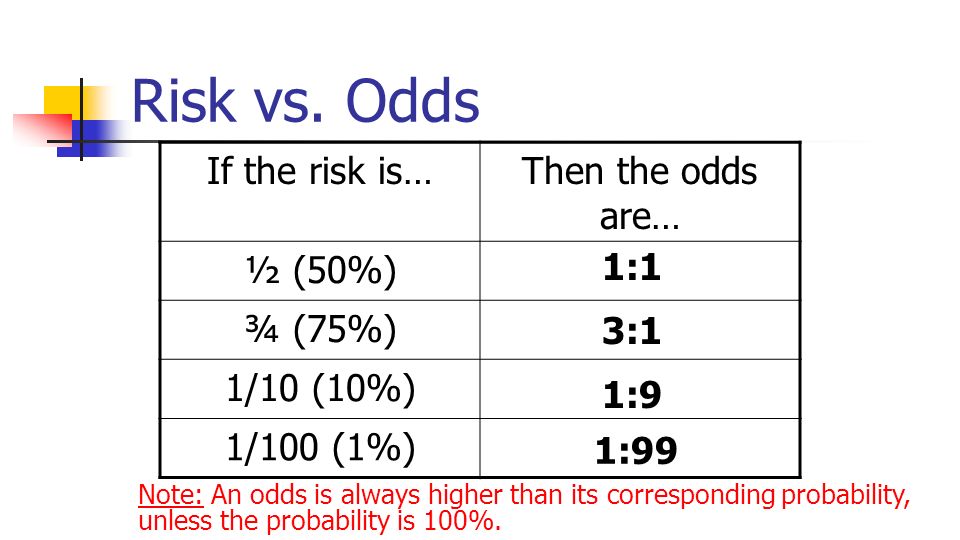
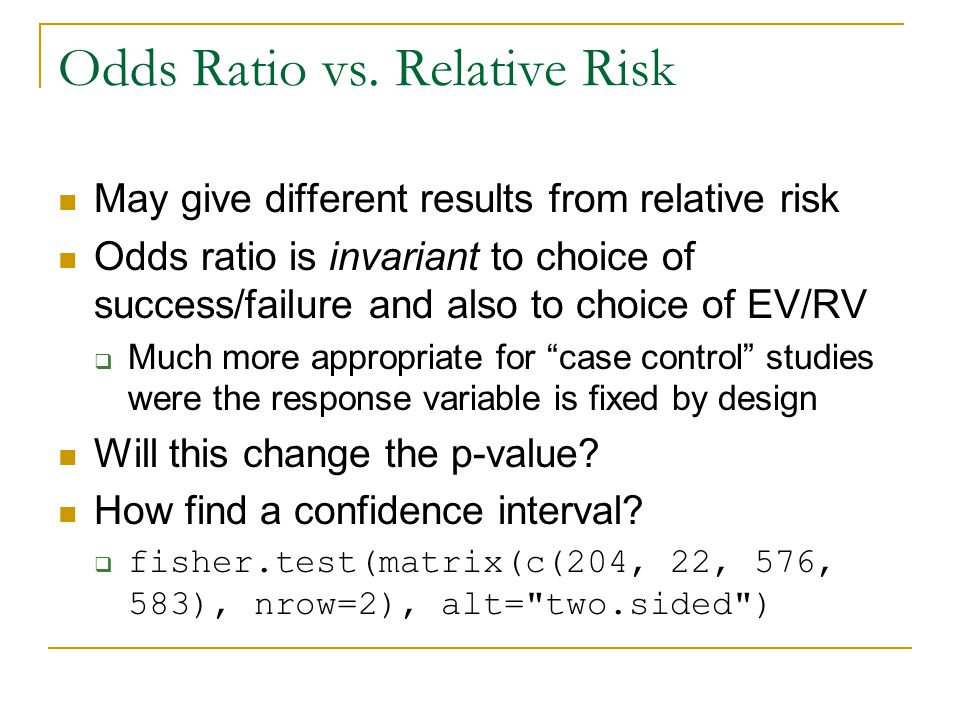
The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programAnd a risk of 095 is equivalent to odds of 19
Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table Odds are another way of expressing the likelihood of "success" You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with nonsmokers) Remember that in a true casecontrol study one can calculate an odds ratio, but not a risk ratio However, one can calculate a risk difference (RD), a risk ratio (RR), or an odds ratio (OR) in cohort studies and randomized clinical trials




Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Odds of dying estimates assume that mortality trends change slowly over time with changes of only a few percentage points from year to year Currently, COVID19 trends are changing too rapidly to confidently anticipate future risk levels Visit the Injury Facts COVID19 page to track realtime data in the United States COVID19About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators This brings us to today's topic Odds Ratio (OR) vs Relative Risk (RR) Odds vs Probability why we love them and why these two cousin statistics continue to confuse us Anyone with a math, science, or medical background has been taught this, and if
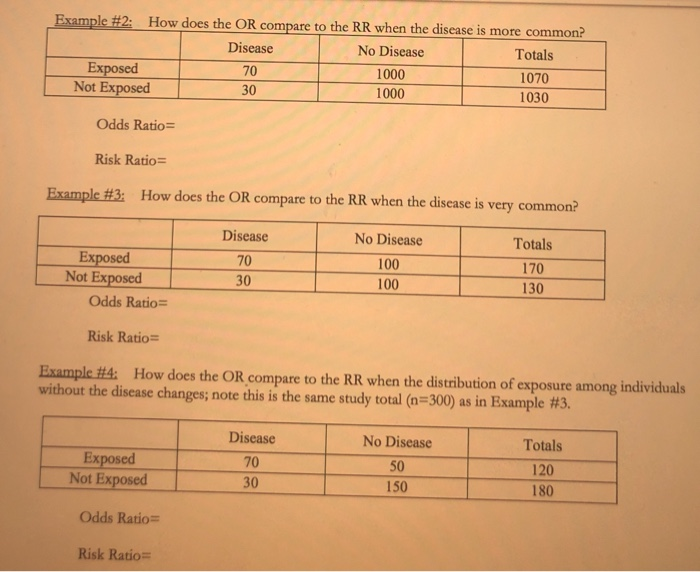



Solved Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com



1
The odds ratio of the second population relative to the first is (1/4)/(1/9) = 225, ie a ratio of ratios, and roughly, but not quite the same, as the relative riskWhen events are common, as is often the case in clinical trials, the differences between odds and risks are large For example, a risk of 05 is equivalent to an odds of 1; Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;



Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
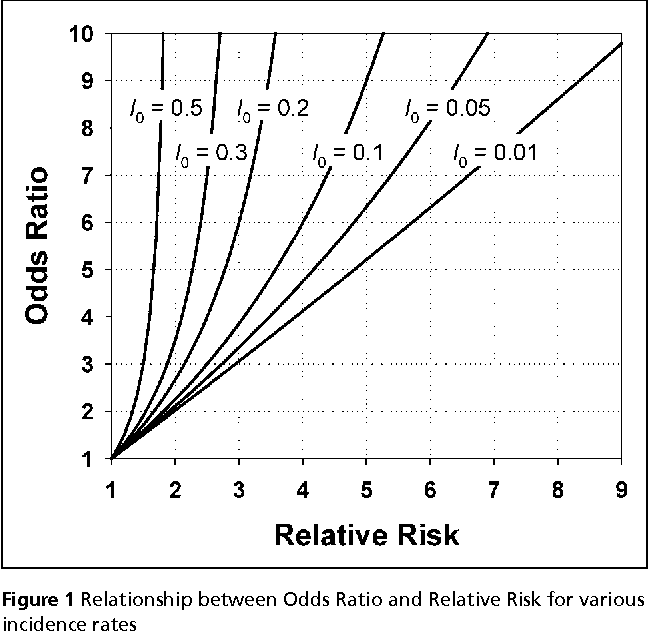
The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225 The reasons a medical article might choose one method of reporting over the other are complex, but the message here is that sorting that out starts by being clear about the difference between probability and odds The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/(c/d) = (ad)/(bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers RR = (a/(ab))/(c/(cd)) = (a(cd))/(c(ab))




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



Rpubs Com
The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the odds of another EssoeOdds1Use the data in Table 315 to calculate the risk and odds ratios Risk ratio 50 ⁄ 10 = 50 Odds ratio Notice that the odds ratio of 52 is close to the risk ratio of 50 That is one of the attractive features of the odds ratio — when the health outcome is uncommon, the odds ratio provides a reasonable approximation of the risk ratio For instance, odds are a symmetric measure, meaning that while risk only examines outcomes given interventions, odds can also examine interventions given outcomes Thus, a study can be constructed where, rather than choosing trial groups and measuring outcomes, outcomes can be chosen, and other factors can be analyzed




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Risk Difference Wikipedia
The relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks isAbsolute risk, attributable risk, attributable risk percent, population attributable risk percent, relative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technicalRisk Ratio vs Odds Ratio As explained in the "Motivating Example" section , the relative risk is usually better than the odds ratio for understanding the relation between risk and some variable such as radiation or a new drug



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology
Pute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greaterA fractional listing of 6/1 (sixtoone) odds would mean that you win $6 against every $1 you wager, in addition to receiving your dollar back (ie, the amount you wagered)2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Odds versus risk Odds versus risk For instance, odds are a symmetric measure, meaning that while risk only examines outcomes given interventions, odds can also examine interventions given outcomes Thus, a study can be constructed where, rather than choosing trial groups and measuring outcomes, outcomes can be chosen, and other factors can beOdds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 4125 Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C) The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group It is calculated as Relative risk = A/ (AB) / C/ (CD) In short, here's the difference An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds



Github Flor3652 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Shiny App




Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators The terms 'risk' and 'odds' are often used interchangeably but they actually have quite different implications and are calculated in different ways Odds is a concept that is very familiar to gamblers It is a ratio of probability that a particular event will occur and can be any number between zero and infinityRisk factor for the disease • Less than 10 indicates that the odds of exposure among casepatients are lower than the odds of exposure among controls The exposure might be a protective factor against the disease The magnitude of the odds ratio is called the "strength of the association" The further away an odds ratio is



印刷可能 Odds Vs Risk ただの悪魔の画像



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probabilitySometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4The risk ratio In practice, risks and odds for a single group are not nearly as interesting as a comparison of risks and odds between two groups For risk you can make these comparisons by dividing the risk for one group (usually the group exposed to the risk factor) by the risk for the second, nonexposed, group This gives us the risk ratio




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
Calculation of probability (risk) vs odds In statistics, odds are an expression of relative probabilities, generally quoted as the odds in favor The odds (in favor) of an event or a proposition is the ratio of the probability that the event will Odds Ratios vs Risk Ratios Posted on by StatsBySlough From the previous post, we understand that Odds Ratios (OR) and Risk Ratios (RR) can sometimes, but not always be interpreted in the same way We even saw that scientific studies made the mistake of interpreting odds ratios as risk ratios The odds ratio is a common measure of risk but its interpretation may be hazardous The risk ratio is a ratio of probabilities, which are themselves ratios The numerator of a probability is the number of cases with the outcome, and the denominator is the total number of cases




Odds Ratio Vs Number Of Risk Protective Alleles For Breast Cancer Download Scientific Diagram




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions



Bryan Carmody For M2s Preparing For Usmle Step 1 Epidemiology Questions Are Free Points You Don T Have To Make 2x2 Tables Or Memorize Formulae From First Aid To Calculate Or



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream




Measures Of Effect Risk Ratio Vs Rate Ratio Risk Factors Disease Rare Disease




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




1 A Comparison Of Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio With The Average Marginal Download Scientific Diagram



Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




The Binomial Applied Absolute And Relative Risks Chisquare




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk



Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1







Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Effect Size Odds Ratio Or Vs Relative Risk Rr Youtube




いろいろ Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk ただの悪魔の画像




The Unadjusted And Adjusted Odds Ratio Of The Association Between Risk Download Scientific Diagram




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Measuring Of Risk




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology




いろいろ Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk ただの悪魔の画像



Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08




Solved Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Calculation And Interpretation Of Odds Ratio Or And Risk Ratio Rr Youtube



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratios Of Risk Factors For The Severity Of Cad By Ethnicity Odds Download Scientific Diagram



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




The Odds Of Dying Perceived Risk Vs Reality Insure Info Blog



Polygenic Risk Scores Odds Ratios Vs Beta Coefficients Bioinformatics



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Casecontrol Studies For Outbreak Investigations Goals N N




Risk Factors And Disease Profile Of Post Vaccination Sars Cov 2 Infection In Uk Users Of The Covid Symptom Study App A Prospective Community Based Nested Case Control Study The Lancet Infectious Diseases




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



File Probability Vs Odds Svg Wikimedia Commons




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08



Attributable




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




Odds Ratios From Univariate Regression Model Of Oasis Vs Risk Factors Download Table
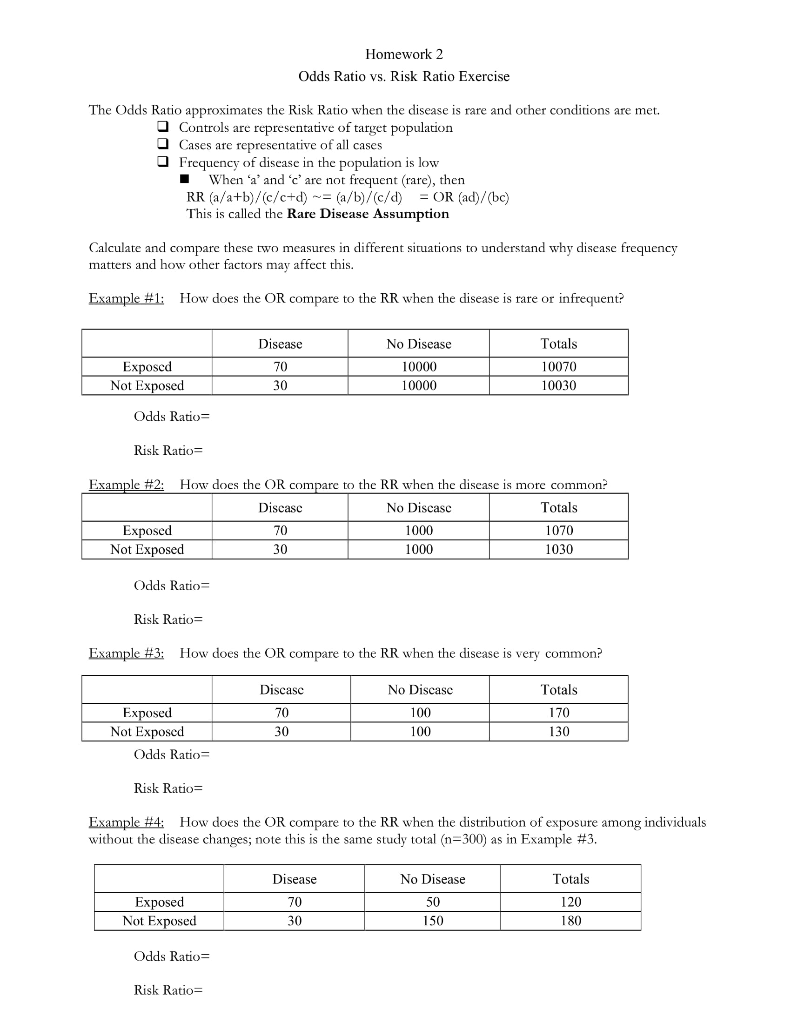



Solved Homework 2 Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Chegg Com
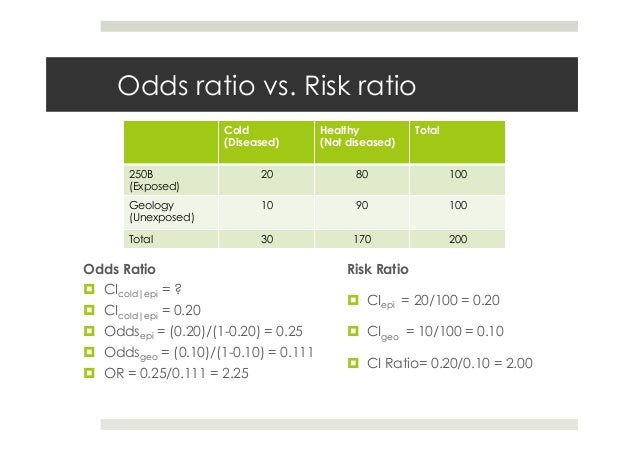



14 Lab Slides Mo A




Www Thesun Co Uk Wp Content Uploads 21 06 Betting France V Switzerland Jpg Strip All Quality 100 W 10 H 800 Crop 1



File Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Svg Wikimedia Commons
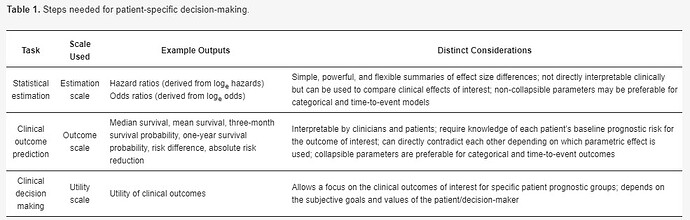



Should One Derive Risk Difference From The Odds Ratio Bayes Datamethods Discussion Forum




Comparative Risk Of Acute Kidney Injury Reported As Boxplots For Odds Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube



Odds




Evidencebased Journal Club Intentiontotreat Odds And Risk Paul




Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction



1




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Literature Search




Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Extensive Video Youtube




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo




Solved Present Example Of An Dolds Ratio Compared To A Chegg Com




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像
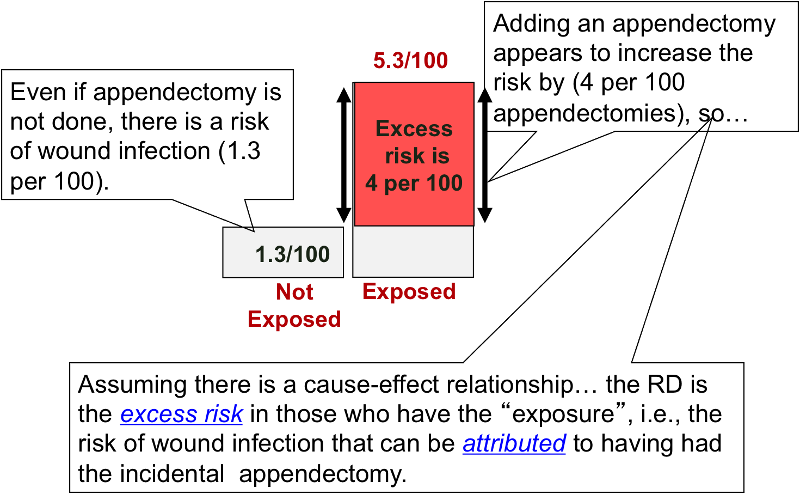



Risk Differences And Rate Differences



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿